Core Features
Introduction
Neosync ships with a number of features but there are four core features that drive Neosync.
Anonymization
Neosync provides the core anonymization functionality through transformers. Transformers anonymize or mask source data in any way you'd like. Neosync ships with a number of pre-built transformers to help you get started or you can write your own user defined transformer.
You can use the prebuilt Neosync transformers in order to anonymize your sensitive data or generate new data that looks just like your production data. The Schema page is where you can select, at the column level, how you want to anonymize your data.
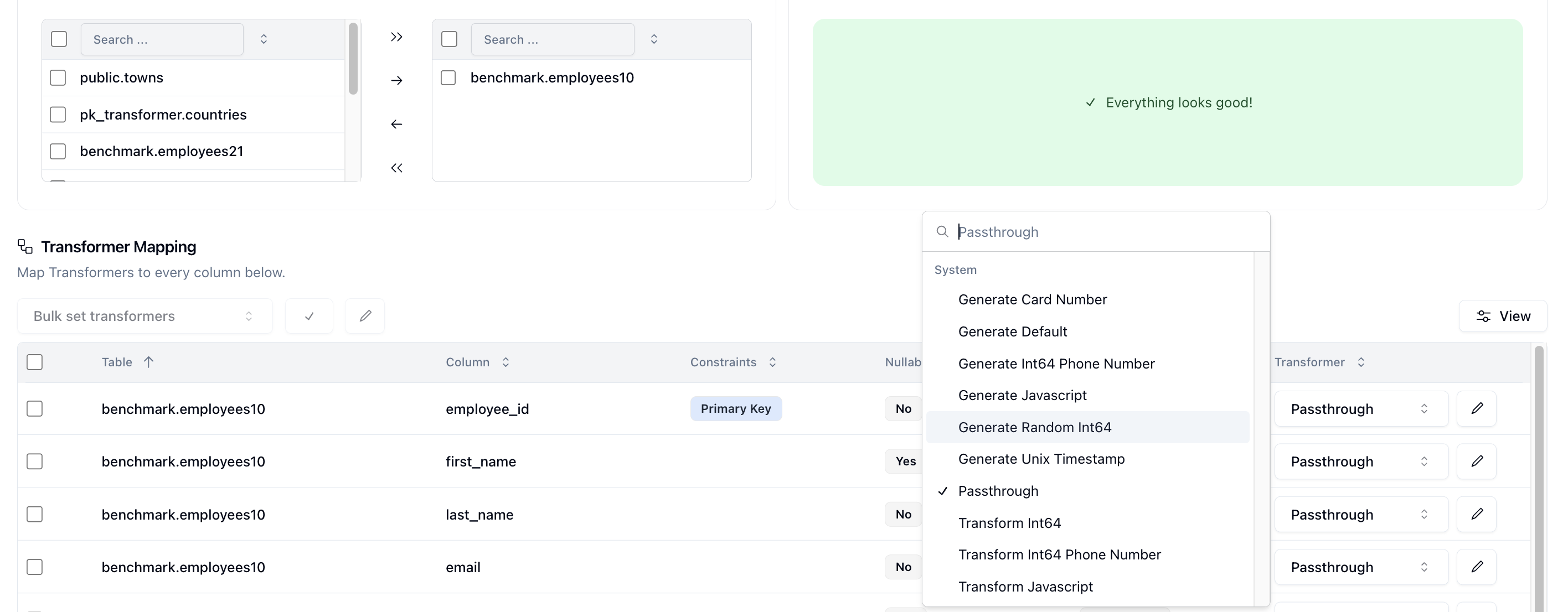
You have full control over how you configure your schema and can even create your own transformer with your own custom transformation logic if you wish to do so. Neosync is a powerful anonymization engine that can deliver a better developer experience for engineering teams.
Synthetic Data Generation
Synthetic data can be useful for testing applications and services in unsecure development and stage environments where you don't want your sensitive data to be floating around. Neosync helps teams create high-quality synthetic data from their production data that is representative of that production data using our transformers. There are multiple ways to generate high quality synthetic data that can be useful depending on the use-case.
Neosync can generate synthetic data from scratch, making it easy to test new features that don't already have generated data or when the current production data is to sensitive to work with. We give you different options to be able to generate synthetic data so that it fits your schema and works with your applications. These options are transformer specific and will depend on the data being generated. You can easily seed an entire database with synthetic data using Neosync to get started or create synthetic data for just a given column.
Neosync also supports integrating with LLM providers such as OpenAI, Anthropic, TogetherAI and more to deliver AI-generated synthetic data.
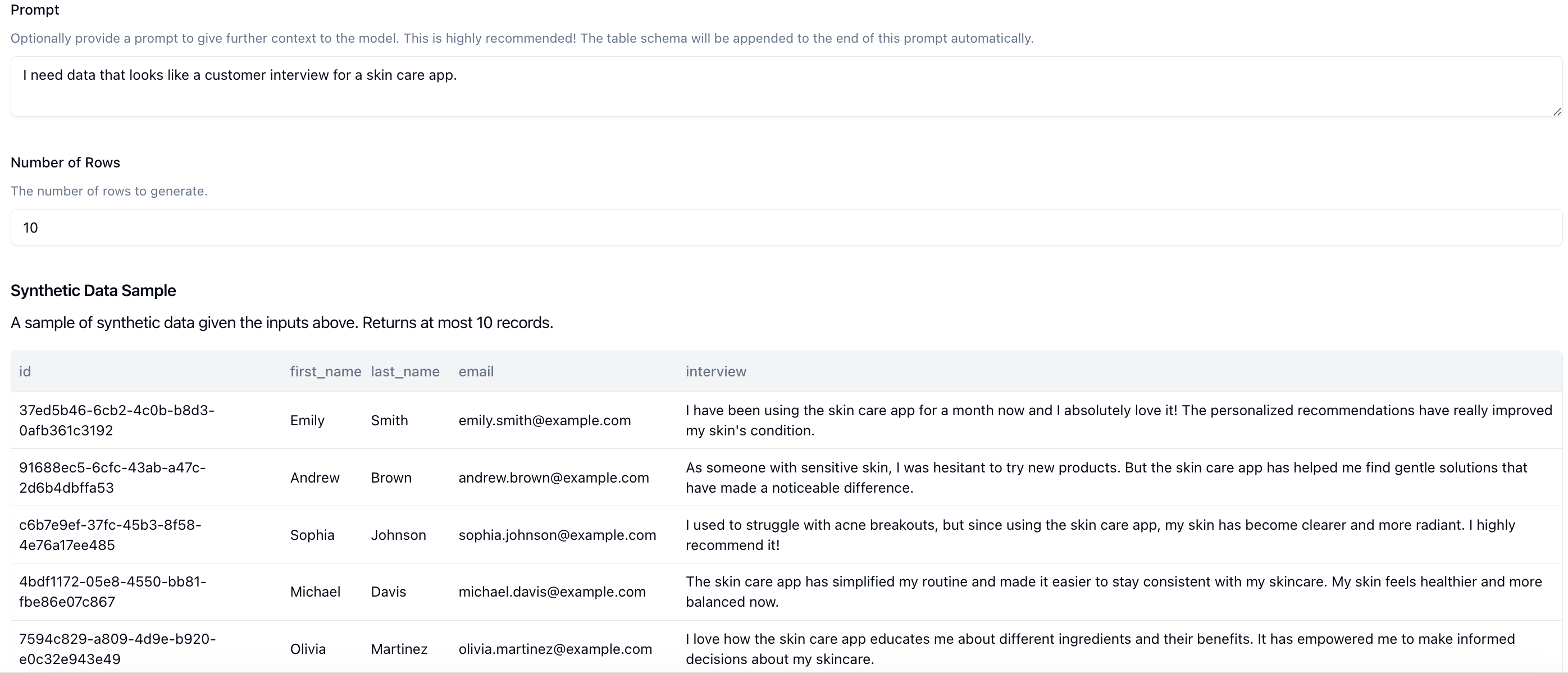
Generating synthetic data is important in order to test services and applications while protecting your sensitive data. Neosync supports many different kinds of synthetic data generation, from full synthetic data generation to partial synthetic data generation across most data types.
Subsetting
Subsetting is useful to reduce the size of a large dataset so that it is usable in another environment with less resources. For example, if you have a large 100gb database, you'll likely want to filter that down to be able to use it locally.
Neosync can help you subset your data by taking in a SQL statement of how you want to filter your data on a table-by-data. This gives you a flexible way of building your destination data set. Once you've connected Neosync to your source database and configured your schema and mappings, you can then decide to subset that data further by selecting a source table to start with.
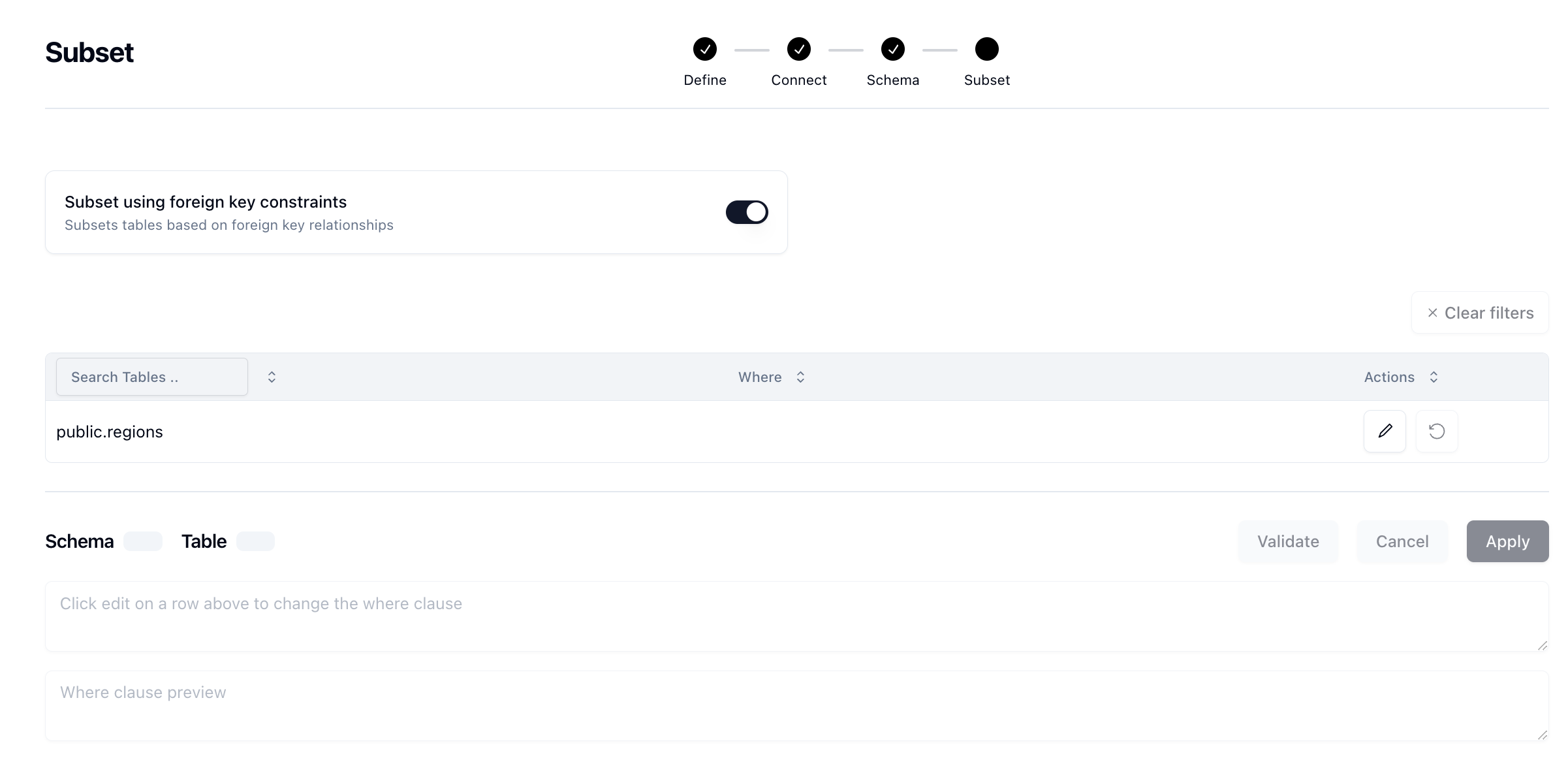
Neosync will automatically ensure relational integrity in the data, making sure that the resulting dataset, post-subset, still has all of the foreign key constraints you had in the original data set. Additionally, Neosync can subset self-referencing tables and circular dependencies, provided there is at least one nullable column within the circular dependency cycle to serve as a viable entry point in your database schema.
Once you've subsetted the data, Neosync will push the result set to your destination(s).
Neosync has powerful subsetting features which allow you to create smaller subsets of your data while maintaining relational integrity. This is useful for local and CI testing where you don't want or need the entire dataset but don't want to spend time querying, joining and filtering the data yourself.
Orchestration
At it's core, Neosync is an orchestration platform with anonymization, synthetic data and subsetting capabilities. We rely heavily on Temporal for our orchestration backbone as it provide us with a lot of power out of the box.
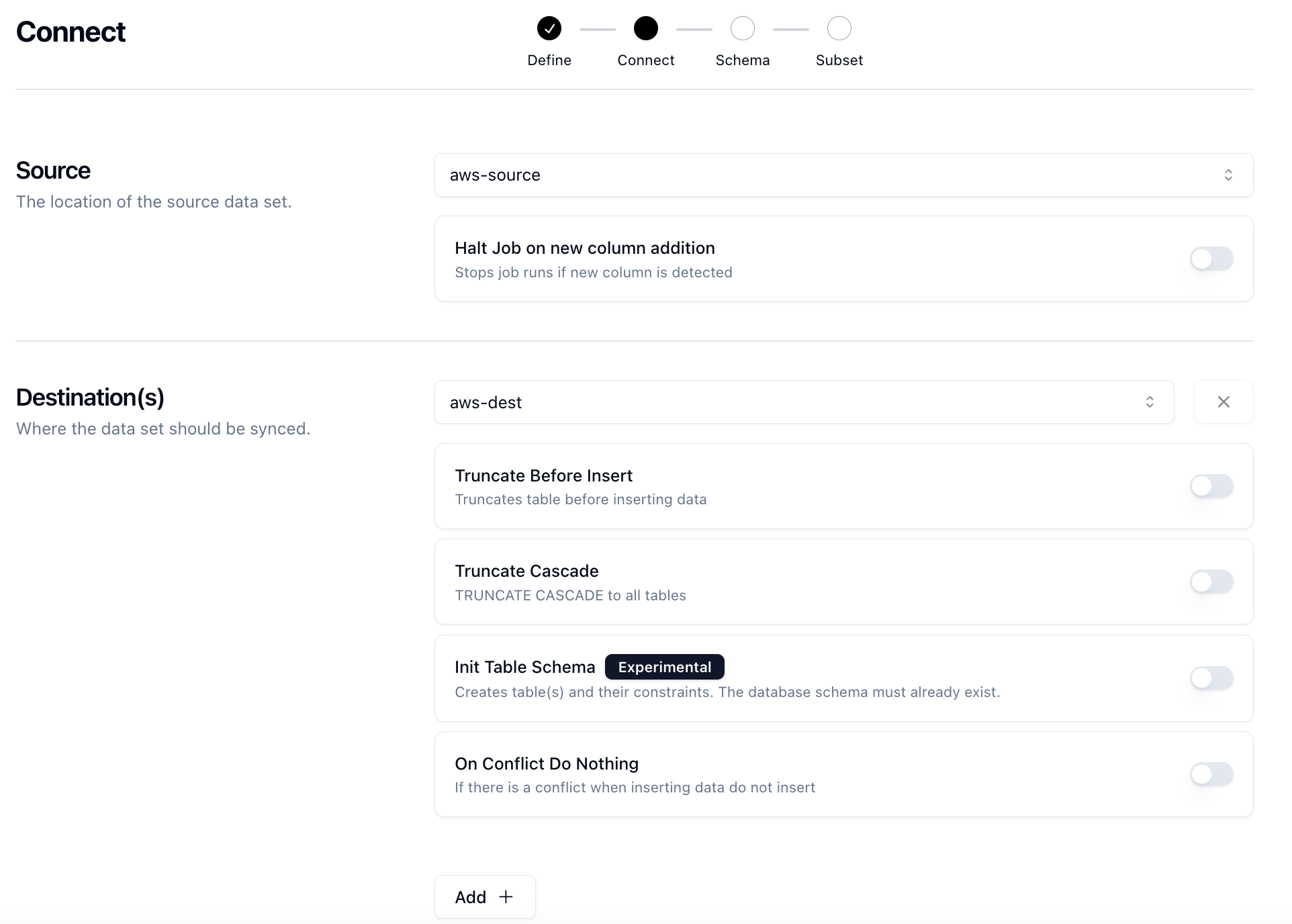
Depending on the type of Job you create, you can sync data from a source database to one or many destination databases. This is where the orchestration comes into play.